Forest degradation as bad for climate as deforestation, says report
Sophie Yeo
04.08.15Sophie Yeo
08.04.2015 | 5:40pmDegradation of tropical forests could be as severe a problem as full-scale deforestation when it comes to their carbon emissions.
While not as widely recognised within policymaking circles, the steady deterioration of forests across places such as the Amazon and Borneo could be responsible for 6-14% of all human-caused emissions.
This is the finding of a new review into the state of the world’s tropical forests, conducted by the International Sustainability Unit, a charity backed by Prince Charles.
The problem demands a re-evaluation of forest policy, which leans towards stemming deforestation as the key to curbing tropical forest emissions, says the report.
Carbon Brief looks at the role of forests in curbing climate change.
High emissions
Tropical deforestation is a major driver of climate change. In areas such as the Amazon, forest ecosystems absorb and store carbon, and cutting them down emits between 2.9 and 3.3 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide* every year, or around 8% of the global total, the report says.
But deforestation is only part of the story. In addition to this, the degradation of tropical forests releases between 2.2 to 5.39 gigatonnes into the atmosphere, or around 6-14% of global carbon dioxide emissions.
This means that total combined emissions from tropical forests comes to between 5.1 and 8.36 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide, or between 14 to 21% of all human-caused emissions (green area, below).
In comparison, 31.5 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide is emitted every year by fossil fuels and cement production (grey area, below).
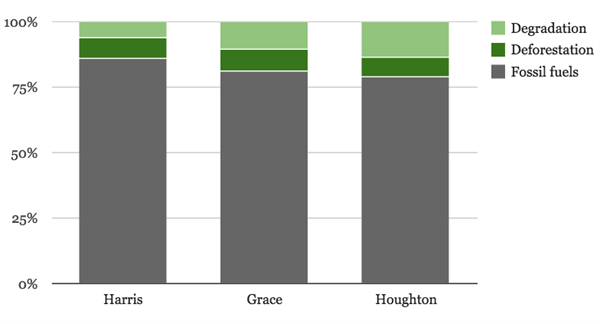
Percentage of annual carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuels and forests. Data from ISU report.
These figures are based on studies led by John Grace of Edinburgh University, Richard Houghton of the Woods Hole Research Center, and Nancy Harris of the World Resources Institute. These rely on three datasets: national inventories of emissions provided to the UN; research into specific plots of forest land; and satellite data.
It is notoriously difficult to account for forest emissions, and the 14 to 21% figure is higher than sometimes reported. The report justifies the increase in this way:
Measuring the rate of emissions from forest degradation is a particularly imprecise art, with the range of the potential volumes varying much more than for deforestation.
This uncertainty is due to a lack of precision in the remote sensing used to detect degradation, difficulties in calculating emissions when the damage to the forest differs widely across different areas, and different studies including varying causes for deforestation, the report says.
Despite the uncertainty, the problem of forest degradation demands a “commensurate policy response”, it adds.
This is because current policy efforts are concentrating on halting deforestation, which nonetheless continues to rise. A 2013 paper estimated that 8.5 million hectares of tropical forest is cleared annually, rising at around 200,000 hectares every year.
For instance, a much-lauded New York Declaration on Forests, backed by both governments and corporations in 2014, pledged to reduce deforestation to zero where possible, while only to significantly reduce degradation.
Meanwhile, Guyana is the only country to have included emissions reference levels for degradation in their UN submissions on forests. Mexico includes a section on degradation in an annex, while Colombia, Brazil and Ecuador include deforestation only.
Yet the figures taken from recent studies suggest that degradation contributes at least 30% of total emissions from tropical forests – and could be as high as 50%. The paper says:
Stephen Cornelius, chief advisor on climate change at WWF UK, tells Carbon Brief that the report’s assessment of how seriously degradation is considered within policy is “broadly right”. He says:
Even within REDD+, the UN’s flagship policy to reduce both deforestation and degradation, there is a disparity in how the two problems are perceived. He says:
Sequestration
The UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change attached a much lower figure to emissions from changes in land use, which is not limited to tropical deforestation, but also includes, for example, boreal forests, peatlands and agriculture. Altogether, these are responsible for around 10% of human emissions, according to the panel.
However, this takes into account the vast potential that forests and other land-based carbon sinks have to absorb and store carbon, as well as release it. The 10% figure represents emissions from land use once its capacity to also absorb carbon dioxide has been accounted for.
However, the ISU report argues that one drawback of this approach is that it hides the much larger figure for the emissions released by destroying forests.
Rising emissions from burning fossil fuels can also create the impression that deforestation is declining, when, in fact, it is simply shrinking as a proportion of the whole.
Taking action to reduce carbon emissions from deforestation and degradation, as well as safeguarding existing tropical forest, could allow forests to take up an additional 12.7 to 14.2 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide, according to the report. Global emissions in 2010 were 49 gigatonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent, and were growing on average at a rate of 1 gigatonnes a year.
One recent study by led by former NASA GISS director James Hansen suggested that, between 2031 and 2080, it would be possible to mitigate an extra 100 gigatonnes of carbon through reforestation. It is an estimate that the ISU says is within the realms of possibility:
Addressing the problem
Why is this significant? Because it could put the world on the path to avoiding dangerous climate change.
Accompanied by a 6% decrease in fossil fuel emissions every year from 2013, this would achieve a decline in carbon dioxide levels to 350 parts per million near the end of the century, according to the Hansen paper. This is the level endorsed by campaigners and some scientists, including former UN science chief Rajendra Pachauri.
Hansen, who put climate change on the map in a 1988 testimony before Congress, also asserts in a 2008 paper that halting deforestation, accompanied by a phase-out of coal by 2030, and limiting other fossil fuel consumption to known reserves in 2007, could hold atmospheric carbon dioxide at 350ppm by the end of the century. This assumes that, after 2030, forests are sequestering carbon dioxide at a maximum rate of 5.9 gigatonnes a year.
Scientists, policymakers and conservationists have long been attempting to stem the destruction of the world’s tropical forests. The New York Declaration on Forests, the Bonn Challenge and the Lima Challenge are three recent initiatives to prompt new action.
But this needs to take into account the underestimated role of degradation.
According to Nigel Sizer, global director of the forests programme at the World Resources Institute, which also tracks deforestation, focus is already swinging in this direction. He tells Carbon Brief:
Addressing deforestation – and a heightened call to arms on degradation – could be a key pillar in tackling climate change over years to come.
Main image: Shennongjia Forestry District, Hubei, China.
*Carbon Brief has converted carbon into carbon dioxide by multiplying by 44 and dividing by 12. Update 09.04.15 - Additional information on the sidelining of degradation in forest policy included


