
Analysis: Nearly 60 countries have ‘dramatically’ cut plans to build coal plants since 2015
Josh Gabbatiss
04.08.25Josh Gabbatiss
08.04.2025 | 1:07pmNearly 60 countries have drastically scaled back their plans for building coal-fired power plants since the Paris Agreement in 2015, according to figures released by Global Energy Monitor (GEM).
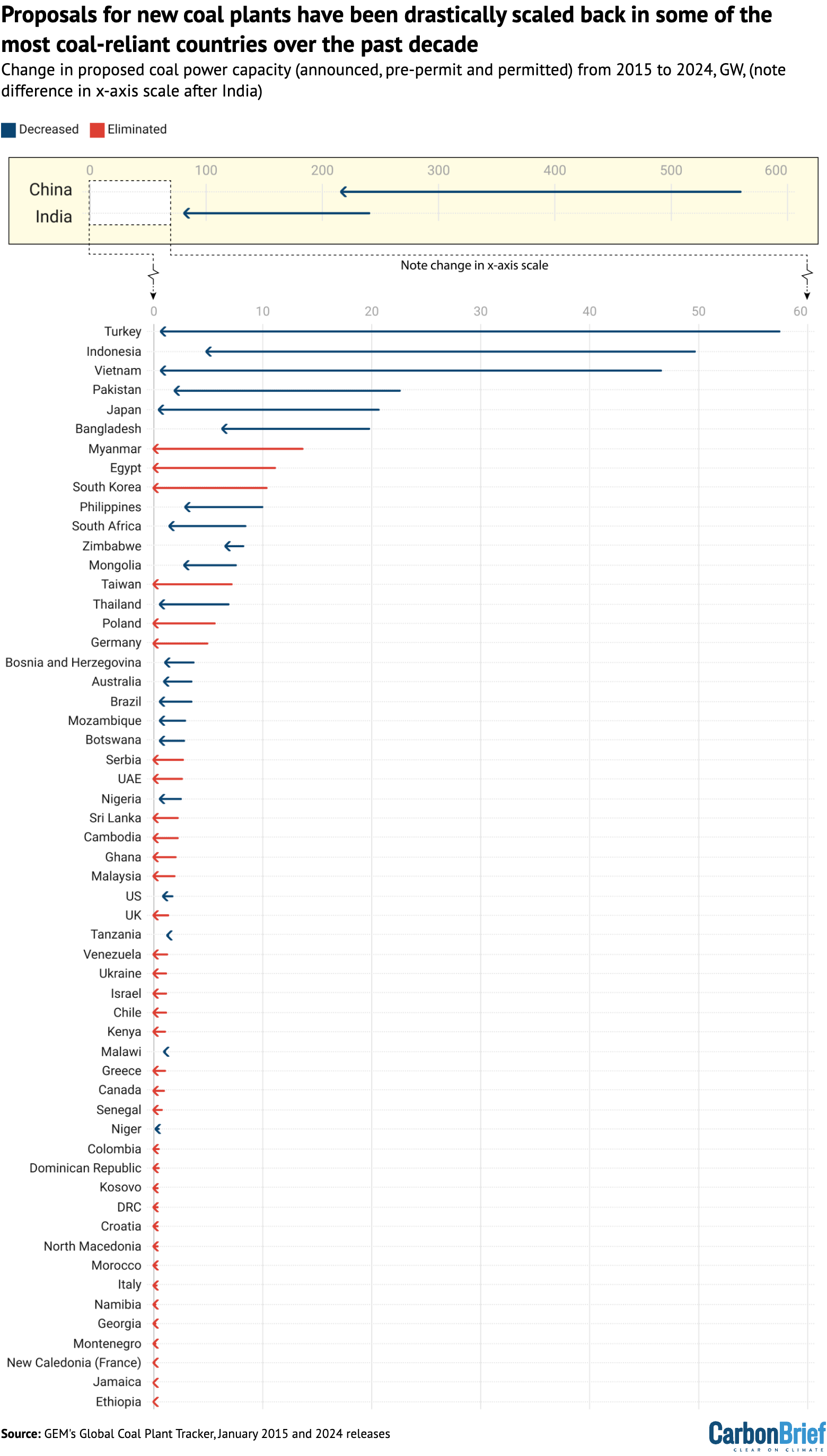
Among those making cuts of 98% or more to their coal-power pipeline are some of the world’s biggest coal users, including Turkey, Vietnam and Japan.
The data also shows that 35 nations eliminated coal from their plans entirely over the past decade, including South Korea and Germany.
Global coal-fired electricity generation has increased since 2015 as more power plants have come online.
But the data on plants in “pre-construction” phases in 2024 shows what GEM calls a “dramatic drop” in proposals for future coal plants.
The number of countries still planning new coal plants has roughly halved to just 33, with the proposed capacity – the maximum electricity output of those proposed plants – dropping by around two-thirds.
China and India, the world’s largest coal consumers, have also both reduced their planned coal capacity by more than 60% over the same timeframe, from a total of 801 gigawatts (GW) to 298GW.
However, both countries still have a large number of coal projects in the pipeline and, together, made up 92% of newly proposed coal capacity globally in 2024.
‘Dramatic drop’
The Paris Agreement in 2015 had major implications for the use of fossil fuels. As the fossil fuel that emits the most carbon dioxide (CO2) when burned, coal has long been viewed by many as requiring a rapid phaseout.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the International Energy Agency (IEA) both see steep declines in “unabated” coal use by 2030 as essential to limit global warming to 1.5C.
But coal power capacity has continued to grow, largely driven by China.
Global capacity hit 2,175GW in 2024, up 1% from the year before and 13% higher than in 2015, according to GEM’s global coal-plant tracker.
This growth disguises a collapse in plans for future coal projects.
GEM’s latest analysis charts a decade of developments since the Paris Agreement and the “dramatic drop” in the number of coal plant proposals.
In 2015, coal power capacity in pre-construction – meaning plants that had been announced, or reached either the pre-permit or permitted stage – stood at 1,179GW.
By 2024, this had fallen to 355GW – a 70% drop. This indicates that countries are increasingly turning away from their earlier plans for a continued reliance on coal.
In total, 23 nations reduced the size of their proposals over this period and another 35 completely eliminated coal power from their future energy plans. Together, these 58 countries account for 80% of global fossil fuel-related CO2 emissions.
The chart below shows these changes, with China and India shown on a different x-axis due to the scale of their proposals. (See section below for more information.)
According to GEM, of the coal plants that were either under pre-construction or construction in 2015, 55% ended up being cancelled, a third were completed and the remainder are still under development.
Many of the nations that have phased coal out of their electricity plans are either very small or only had modest ambitions for building coal power in the first place.
However, the list also includes countries such as Germany and South Korea. These nations are both in the top 10 of global coal consumers, but their governments have committed to significantly reducing or, in Germany’s case, phasing out coal use by the late 2030s.
Turkey, Vietnam and Japan are among the big coal-driven economies that are now approaching having zero new coal plants in the works. All have around 2% of the planned capacity they had a decade ago.
Other major coal consumers have also drastically reduced their coal pipelines. Indonesia, the fifth-biggest coal user, has reduced its coal proposals by 90% and South Africa – the seventh-biggest – has cut its planned capacity by 83%.
Of the 68 countries that were planning to build new coal plants in 2015, just nine have increased their planned capacity. Around 85% of the planned increase in capacity by these nations is in Russia and its central Asian neighbours.
China and India
China is by far the world’s largest coal consumer, with India the second largest.
There was 44GW of coal power added to the global fleet last year. China was responsible for 30.5GW of this while retiring just 2.5GW, and India added 5.8GW while retiring 0.2GW.
Between them, these nations contributed 70% of the global coal-plant construction in 2024.
Nevertheless, there were signs of change as newly operating coal capacity around the world reached its lowest level in 20 years.
China and India have also seen significant drops in their pre-construction coal capacity over the past decade.
In 2015, China had 560GW of coal power in its pipeline and India had 241GW. Both nations have seen their proposed capacity drop by more than 60% to reach 217GW and 81GW, respectively.
While this is a significant reduction, both nations still have more coal capacity planned now than any other nation did in 2015. China’s current 217GW is roughly four times more than the 57GW Turkey was planning at that time.
GEM attributes the “slowdown” in China’s new proposals to the nation’s record-breaking solar and wind growth, which saw more electricity generation capacity installed in 2023 and 2024 than in the rest of the world combined.
As for India, GEM says the “notable declines” in coal proposals and commissions came after a “coal-plant investment bubble that went bust in the early 2010s”.
It notes that India is now “encouraging and fast-tracking the development of large coal plants”. The government has cited the need to meet the large nation’s growing electricity demand, especially due to the increased need for cooling technologies during heatwaves.
As other nations move away from the fossil fuel, coal capacity is likely to become increasingly concentrated in these two nations. Together, they made up 92% of the 116GW in newly proposed capacity last year.





